Know Your Enemy: Bed Bugs Identification, Biology, Feeding, Propagation, Habitats
So you think you've got bed bugs, now how do you know for sure? The simple answer is hiring a pest control professional. If you want to find out on your own, we have created a basic guide to help you.
BEDBUGS FACTS
Bed bugs have been around for thousands of years. The common bedbug, Cimex lectularius, is the most infamous human parasite that feeds on human blood. Bed bugs are most active at night. Their name "bed bug" is derived from the insect's preferred habitat of beds or other areas where people sleep. At some point in the early 1940s, they were mostly eradicated in the developed world, but have recently increased in prevalence since 1995.
Bedbug Identification
Bedbug Adults
 Adult bedbugs are flat small disc shaped creatures, and if fed are reddish-brown in color and may be slightly larger right after a blood meal, or a paler whitish hue if they unfed for over 10 days. Bed bugs are wingless and have small microscopic hairs running across their bodies creating an appearance of banding. Bed bugs feed only on the blood of humans and warm-blooded animals. Hungry bed bugs can sense the presence of sleeping people by sensing their body heat and CO2 via special sensors located in their antennas.
Adult bedbugs are flat small disc shaped creatures, and if fed are reddish-brown in color and may be slightly larger right after a blood meal, or a paler whitish hue if they unfed for over 10 days. Bed bugs are wingless and have small microscopic hairs running across their bodies creating an appearance of banding. Bed bugs feed only on the blood of humans and warm-blooded animals. Hungry bed bugs can sense the presence of sleeping people by sensing their body heat and CO2 via special sensors located in their antennas.
Bedbug Nymphs
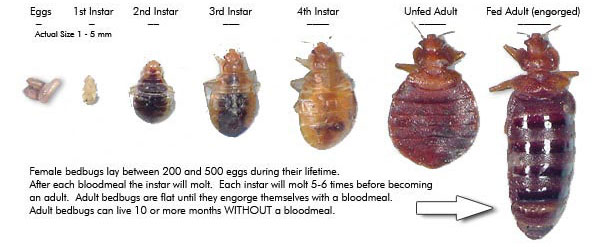
 Bed bugs go through gradual metamorphosis: from egg to nymph to adult. Nymph or "Baby Bed Bug" goes through 5 molts during a 35-48 day nymphal stage. They cast their shed skin each molt. Each nymph requires at least one blood meal to develop to the next developmental instar. Nymphs or baby bed bugs are translucent and white in color and gain their brownish hue as they molt into later stages.
Bed bugs go through gradual metamorphosis: from egg to nymph to adult. Nymph or "Baby Bed Bug" goes through 5 molts during a 35-48 day nymphal stage. They cast their shed skin each molt. Each nymph requires at least one blood meal to develop to the next developmental instar. Nymphs or baby bed bugs are translucent and white in color and gain their brownish hue as they molt into later stages.
Bedbug Eggs
 Female bed bug lays 5-8 eggs per day (200-500 eggs in her lifetime). Eggs of bed bugs are laid individually or in clusters and are cemented to wood, fabrics, or other surface in places where the bed bugs normally hide. Eggs hatch in 6 to 17 days. Eggs are tiny white specs and are very difficult to see. This is often why an infestation only becomes visible in its more severe stages.
Female bed bug lays 5-8 eggs per day (200-500 eggs in her lifetime). Eggs of bed bugs are laid individually or in clusters and are cemented to wood, fabrics, or other surface in places where the bed bugs normally hide. Eggs hatch in 6 to 17 days. Eggs are tiny white specs and are very difficult to see. This is often why an infestation only becomes visible in its more severe stages.
Bedbug Diet
What they eat: Human Blood (i.e. YOU). See the following video how they do that:
When they eat: Peak feeding times typically occure at night (about an hour before dawn) though given the opportunity a bed bug may feed at any time.
How they eat: Attracted by the body temperature of its host, a bed bug will penetrate the skin using two (2) hollow tubes. The first, injects saliva which contains an anesthetic (numbing agent) and an anti-coagulant (a substance that prevents blood clotting making drawing out blood possible). Feeding continues for up to five minutes until the bed bug becomes full.
How Often: Bed bugs like to feed every 5-10 days but can survive up to 18 months without food. Moving out will not help you get rid of bed bugs.
IMPORTANT: Because lesions created by bed bug bites may resemble those of other insects or various allergic reactions, a PEST CONTROL PROFESSIONAL must be present in order to confirm the true presence of bed bugs.
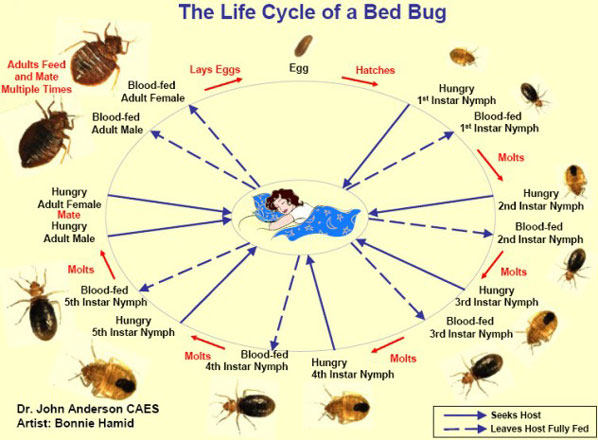
Bed Bug Life Cycle
Female bed bug lays between 200 and 500 Eggs in her lifetime. After hatching an egg becomes a Nymph or "Baby Bed Bug" and undergoes five (5) molting stages called Instrars before becoming a reproductively mature adult (4 weeks to 5 months depending on conditions; on average 5 weeks at room temperature). A bed bug must feed in order to develop into the next stage. After each bloodmeal the instar will molt. Each instar will molt 5-6 times before becoming an adult bedbug. Adult bedbugs can live 10 or more months without bloodmeal.
Bed Bugs Habitats
Bed bugs like warm (70F°+ degrees) protected places such as:
Travel Gear - Luggage, Backpacks, clothing, hotel room furniture, blinds etc.
Bedroom Furniture - Bed bugs will typically be found within a few feet of the host but may travel up to 100 feet to feed. Some common places are seams of the mattress, inside the box spring, headboard, nightstand and other bedside furniture.
Electronics - Home Stereos, smoke detectors, wall clocks, old TV sets, tool boxes etc.
Bed bugs will usually aggregate as a colony in areas near the host. Some tell-tale signs of these colonies are dark clusters of fecal matter (secreted blood), molted bed bug skins which are shed during the maturation stages of a bed bug or in cases of a severe infestation - a musty smell.
Bedbugs infesting mattress:

Bedbugs on electronics:

Bedbugs on carpet:

Bedbugs on furniture:

Bed Bugs Video
For more information on bedbugs watch this wonderful video by the National Geographic Channel:
Please call us at 866-262-9125 to ask about our FREE consultation on bedbug inspection and complete removal.

